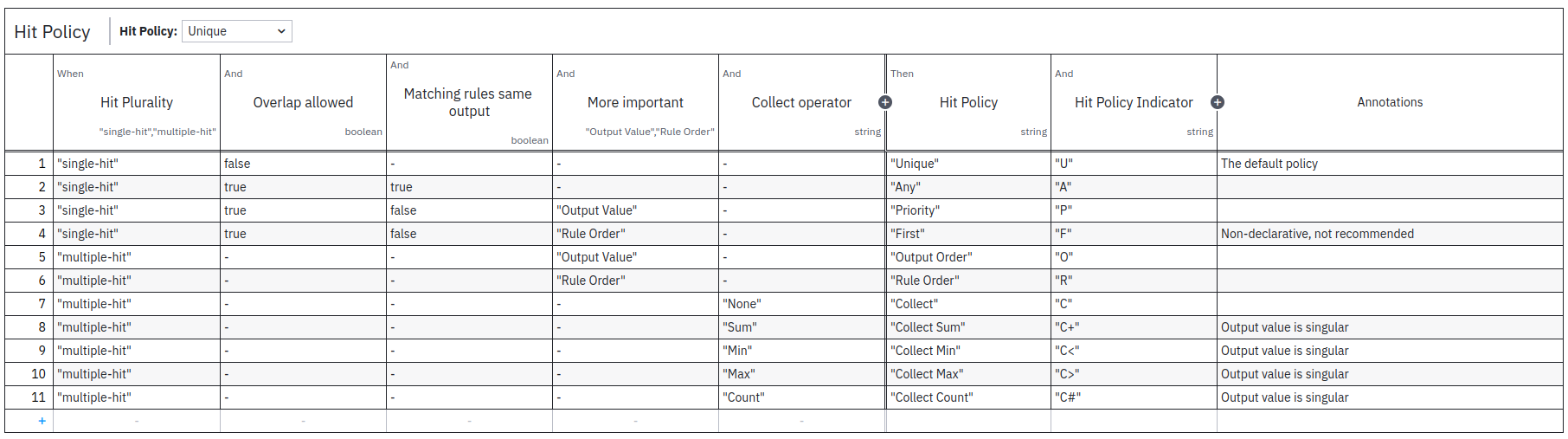
Decision Tables
The World’s Most Famous Decision Modelling Technique
Good to Know
-
DMN’s decision tables are unambiguous: automatic interpretation and execution is possible
-
Inputs are always combined with the and operator!
-
Their entry expressions may specify or (comma separated) to match any of the values in a single rule
-
To express an or within a rule, use additional rule(s)
-
-
Rules cannot be split further, they are the smallest unit of logic after an expression
-
Decision logic is declarative: it describes what, but not how and order of evaluation (rules and inputs) should not matter